How to Sync Your CGM to Any Smartwatch
Mar 13, 2025
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has revolutionized diabetes management by delivering real-time insights into glucose trends. Now, integrating CGM data with a smartwatch takes convenience a step further—offering quick glucose checks during workouts, classes, meetings, or any time you’d rather not reach for your phone.
This concise guide is designed for endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and people living with diabetes who want to explore smartwatch connectivity for various CGMs (FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom, Guardian, and more) across various smartwatches like Apple Watch, Wear OS, and Garmin. From official apps to open-source workarounds, you’ll learn how to set up glucose tracking on your wrist, troubleshoot common pitfalls, and empower your diabetes management with at-a-glance data—wherever you go.
Get Access To Updated Diabetes Technology Courses
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Important Disclaimers
- Overview of Smartwatch Platforms
- Apple Watch
- Wear OS (Samsung/Google/Other)
- Garmin
- Other Proprietary OS Watches (Huawei, Amazfit, MiBand, Fitbit)
- Key Smartwatch Terminology
- Apple Watch Terminology
- Samsung Galaxy Watch Terminology
- Garmin Watch Terminology
- Step-by-Step: Syncing CGM Data to Your Smartwatch
- FreeStyle Libre (Pro)
- FreeStyle Libre 2 (Plus)
- FreeStyle Libre 3 (Plus)
- Dexcom G6
- Dexcom ONE
- Dexcom G7
- Dexcom ONE Plus
- Guardian 3 / 4
- Simplera CGM / Sync
- Other CGMs
- The Present and Future of Direct CGM-to-Smartwatch Connectivity
- The Dream of Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
- Practical Considerations & Troubleshooting
- Conclusion and Additional Resources
1. Introduction
Smartwatches have emerged as valuable health companions for people with diabetes. Glucose readings from a CGM on the wrist facilitate quick checks—especially during exercise, classes, meetings, or anywhere it might be inconvenient to pull out a phone. While not all CGM manufacturers offer native smartwatch integration, a variety of solutions exist, including third-party or open-source software.
In this article, we break down how to link ten common CGMs to popular smartwatches:
- FreeStyle Libre 1 (Pro)
- FreeStyle Libre 2 (Plus)
- FreeStyle Libre 3 (Plus)
- Dexcom G6
- Dexcom ONE
- Dexcom G7
- Dexcom ONE Plus
- Guardian 3 or 4
- Simplera CGM / Sync
- Other CGMs
We will outline compatibility with the most commonly used smartwatches and operating systems, such as:
- Apple Watch (watchOS)
- Wear OS (Samsung Galaxy Watch, Google Pixel Watch, Fossil, Montblanc, TAG Heuer, newer Xiaomi and Fitbit models)
- Garmin (GarminOS)
In many cases, solutions exist for other watch platforms (Huawei, Amazfit, Fitbit, MiBand) via community-driven apps or open-source integrations, although these can be less straightforward.
2. Important Disclaimers
#1 Medical Advice
This document is informational only. It does not replace medical advice, nor is it endorsed by any CGM manufacturer or regulatory authority. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
#2 Open-Source Software
Many methods described here rely on open-source apps like xDrip+, Juggluco, Shuggah, Diabox, etc. These are not approved or supported by CGM manufacturers or any medical agency. Their use is at your own risk.
#3 Accuracy Considerations
- Third-party open-source apps may use custom algorithms and can produce readings that vary slightly from official CGM apps. When in doubt, confirm your glucose with a fingerstick meter.
- Please be aware that open-source apps are not approved for insulin-dosing decisions.
#4 Data Sharing & Cloud Platforms
Most open-source apps do not send your data to official websites like LibreView or Dexcom Clarity. But they may work with Nightscout or Tidepool.
- Nightscout: You must set up an account yourself.
- Tidepool: Offers a free account for users and doctors.
If your healthcare provider needs to see your glucose reports, talk about the best way to share them. Some healthcare providers do not know Nightscout or Tidepool, so they may need help to access your data.
#5 App & OS Updates
- Software and firmware updates can sometimes stop apps from working correctly. To avoid problems, it’s best to turn off automatic updates for your operating system (OS). Only update when your community confirms that everything works well.
- If you have issues after an update, check online communities for the latest fixes and solutions.
3. Overview of Smartwatch Platforms
Apple Watch

Renowned for tight iOS integration and advanced health features.
- Operating system: watchOS version 11.3.1 (as of Feb 2025), with frequent minor updates.
- Key Health Features: ECG, blood oxygen measurement, atrial fibrillation and sleep apnea detection, emergency alerts, VO₂max estimates.
- Battery Life: ~18 hours (standard) to ~36 hours (Ultra models).
- Price Range: $219 (SE) to $799 (Ultra).
Wear OS (Samsung / Google / OnePlus / Fossil / etc.)

Google’s smartwatch platform, popular with Android users.
- Operating system: Wear OS, currently at version 5.0 (based on Android 13).
- Key Features: Google Fit, third-party apps, wide style/price range ($180-$400).
- Battery Life: ~1-3 days (some models up to 4 days).
Garmin

Primarily favored by fitness enthusiasts and outdoorsy users.
- Operating system: GarminOS, proprietary system with updates via Garmin Connect.
- Key Features: Excellent battery life (7-34 days, sometimes solar-assisted), advanced fitness metrics, rugged design.
- Price Range: $299-$599.
Other Proprietary OS Watches

- Operating system: Proprietary operating systems developed by the manufacturer.
- Advantages: Often more affordable, sometimes with very long battery life.
- Drawbacks: Fewer third-party CGM integration options, requiring specialized or community-driven solutions.
4. Key Smartwatch Terminology
Understanding where your CGM data appears on your smartwatch is important. Different watch brands use different terms, so here’s a simple guide.
Most smartwatches use a touchscreen with one or more buttons for control. Some models have a rotating bezel around the screen or crown that can turn to adjust settings. Others, especially rugged or sport-specific watches, rely only on buttons instead of a touchscreen. This variety in controls helps manufacturers design watches for different users and situations.
Apple Watch Terminology
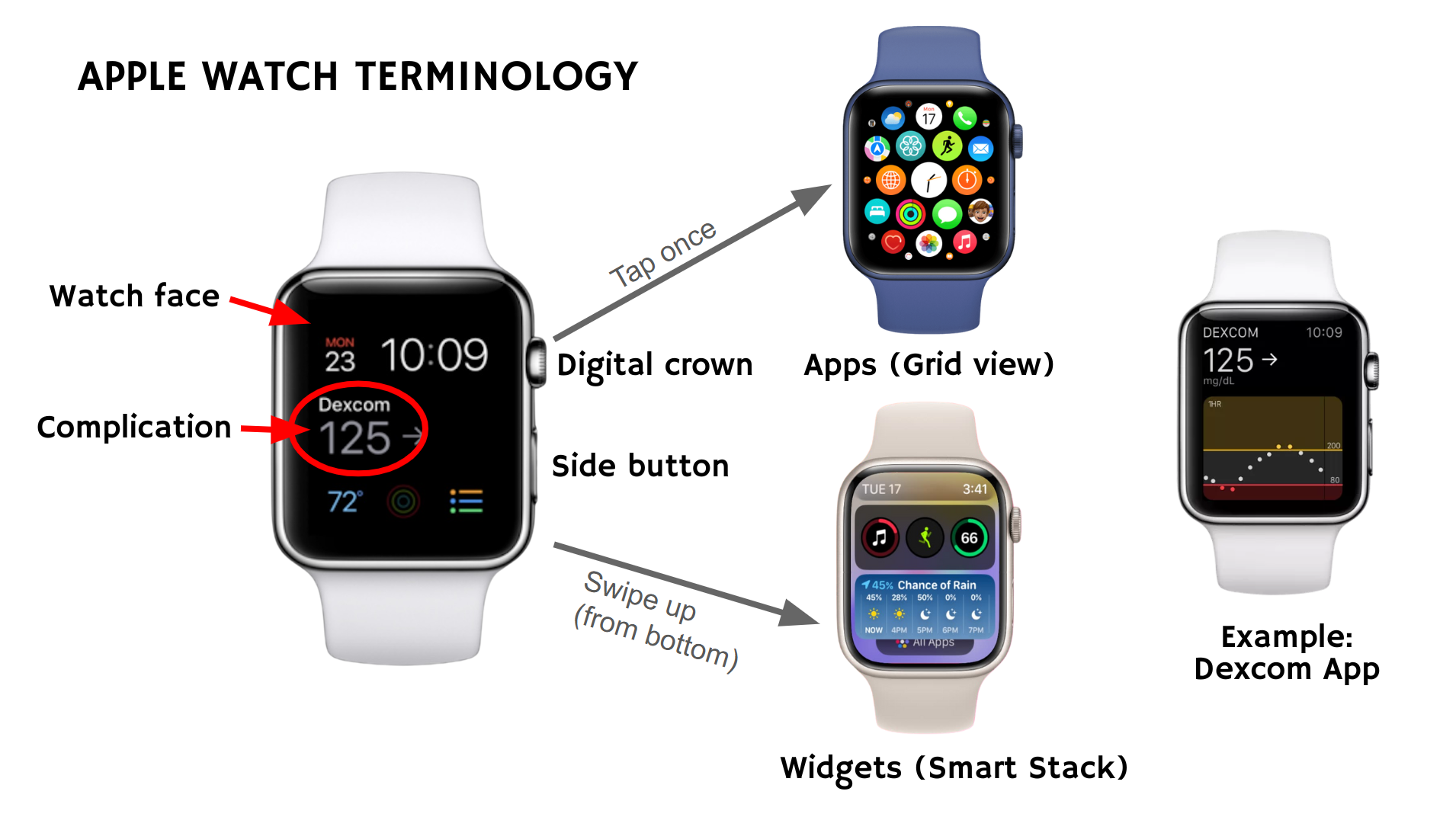
- Watch face: The main screen showing time and other info. Customize by long-pressing the watch face or via the Watch app on your iPhone.
- Complications: Small info “slots” on the watch face that can show real-time data (e.g., glucose).
- Popular modular watch faces that can hold multiple complications are Infograph, Modular, and Modular Duo.
- Apple Watch complications typically refresh only every 15–30 minutes to conserve battery. However, tapping a complication will open the corresponding watch app, where you can view the most recent glucose information in real-time.
- For users of the Shuggah or Gluroo iOS app, there is an additional option to display glucose data as calendar events updating every 5 minutes, providing more frequent visibility of your glucose trends.
- Widgets: In watchOS 10+, accessed by swiping up or using the Digital Crown, part of the “Smart Stack.”
- Apps: The Home Screen shows all preloaded and downloaded apps. Apps can be downloaded from the App Store, either on your Apple Watch or from your iPhone. From the watch face, press the digital crown to see the Home Screen. Tap on an app to open it.
Samsung Galaxy Watch (Wear OS) Terminology
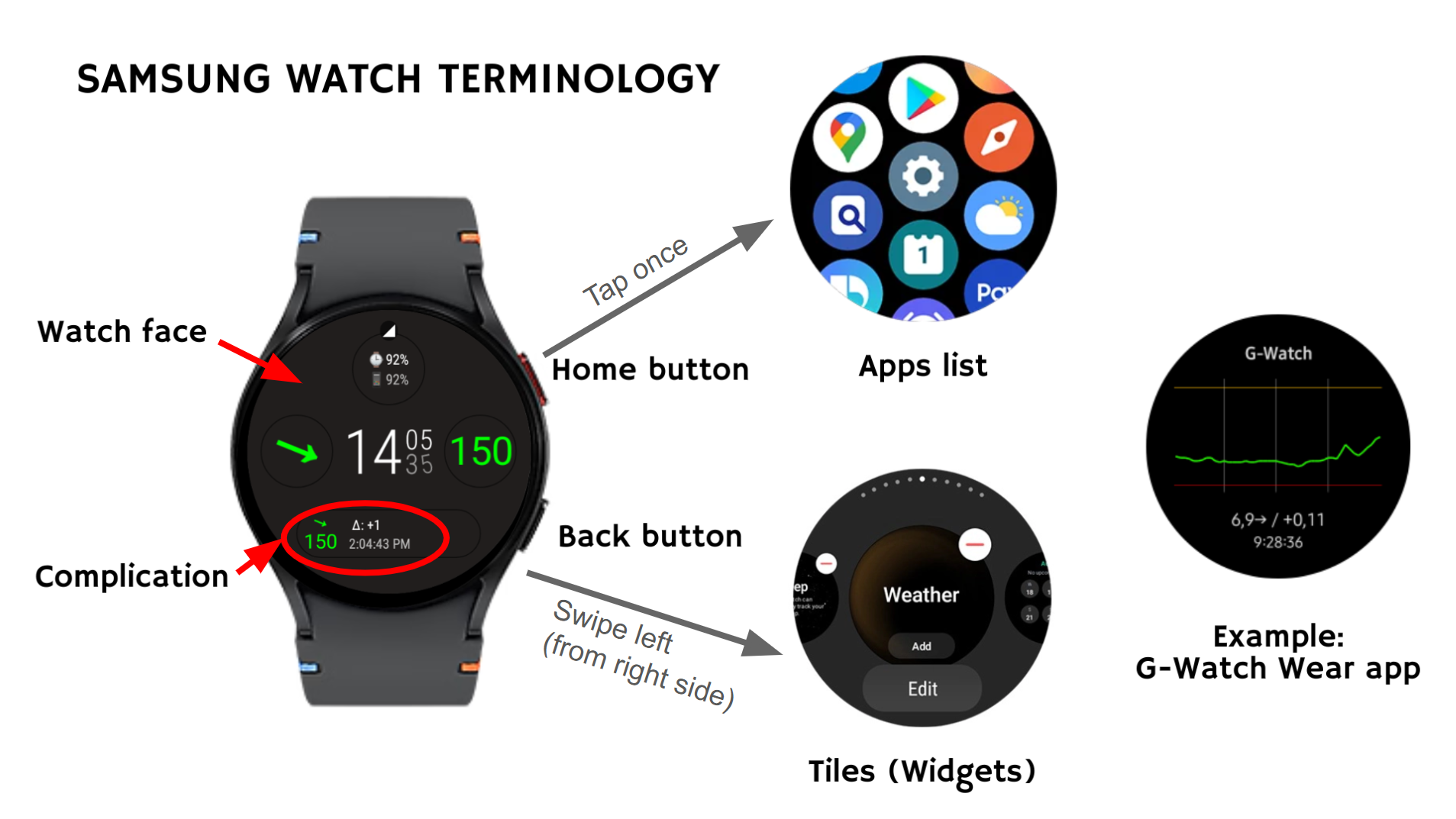
- Watch face: The main screen with customizable designs. Customize by long-pressing the watch face or via the Galaxy Wearable app on your Android phone.
- Complications: Small windows of live data on the watch face (e.g., glucose). Tap to open the full app.
- Tiles (Widgets): Tiles are shortcuts to apps and features that you can add as a screen on your watch. From the watch face, swipe left to see tiles.
- Apps: The Apps screen displays all preloaded and downloaded apps. Apps can be downloaded from the Google Play store, either on your Wear OS watch or from your Android phone. From the watch screen, swipe up from the bottom of the screen to open the Apps screen. Tap on an app to open it.
Garmin Watch Terminology
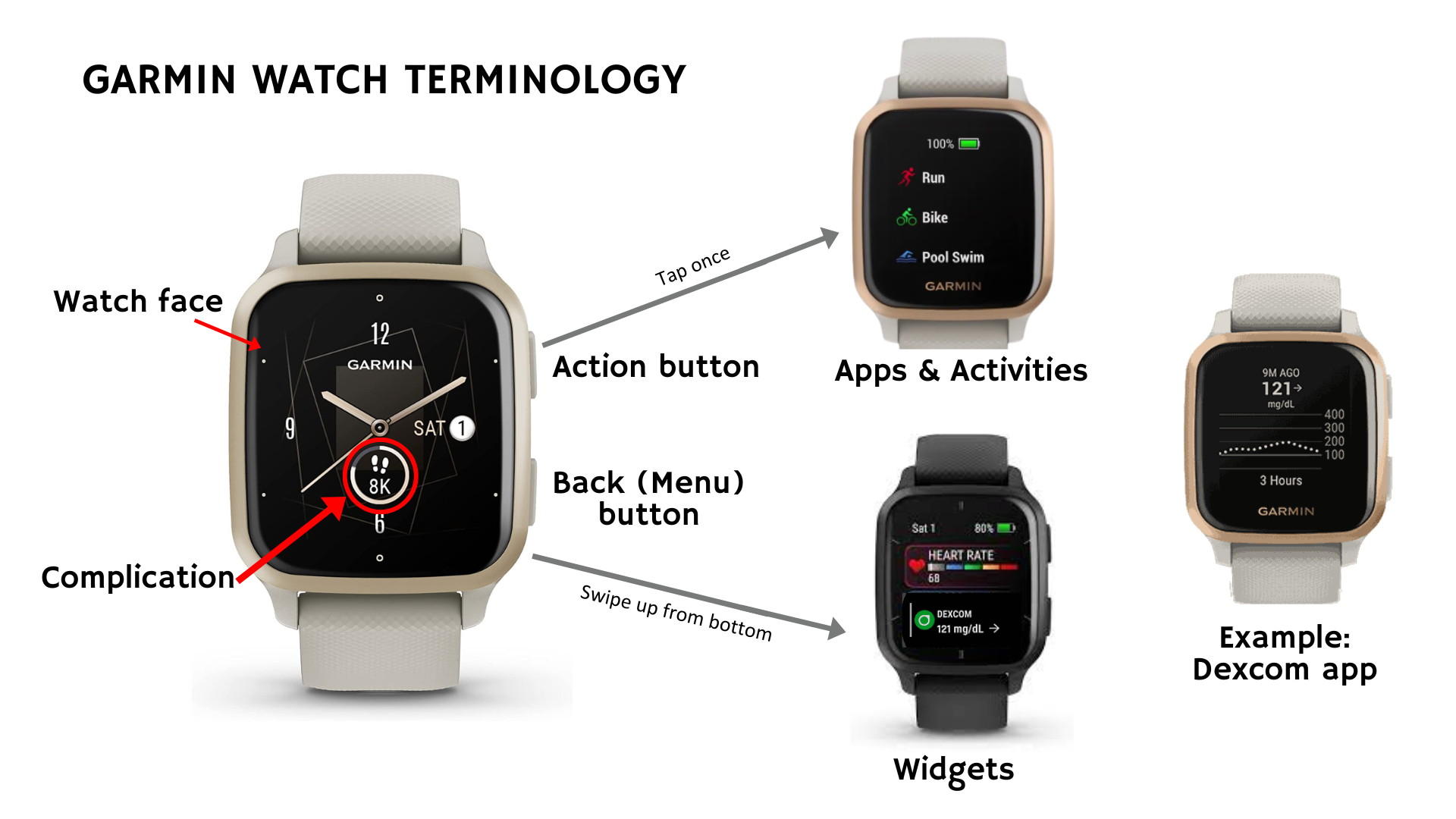
- Watch face: Main display with time and data fields. Customize via long-pressing the Menu button or via the Garmin Connect app on your phone.
- Complications: Small info “slots” on the watch face that can show real-time data from apps, widgets or data fields.
- Widgets: Quick-access screens with at-a-glance information. From the bottom of the watch, swipe up to see the widgets.
- Data Fields: Specific information displayed during activities or on watch faces.
- Apps: Full programs, including third-party watch faces or data fields from the Connect IQ Store. Tap on the Action button to see a list of all apps and activities. Tap on an app or activity to open it.
5. Step-by-Step: Syncing CGM Data to Your Smartwatch
Below are detailed instructions for each CGM type. We emphasize two main categories of solutions:
- Native Integrations: Official apps by CGM manufacturers.
- Open-Source/Third-Party Solutions: Apps like xDrip+, Juggluco, Shuggah, Diabox, and companion watch apps.
Where relevant, we highlight whether an internet connection (via Dexcom Share, LibreLinkUp, etc.) is required, or if it works offline over Bluetooth.
5.1 FreeStyle Libre 1 (Pro)
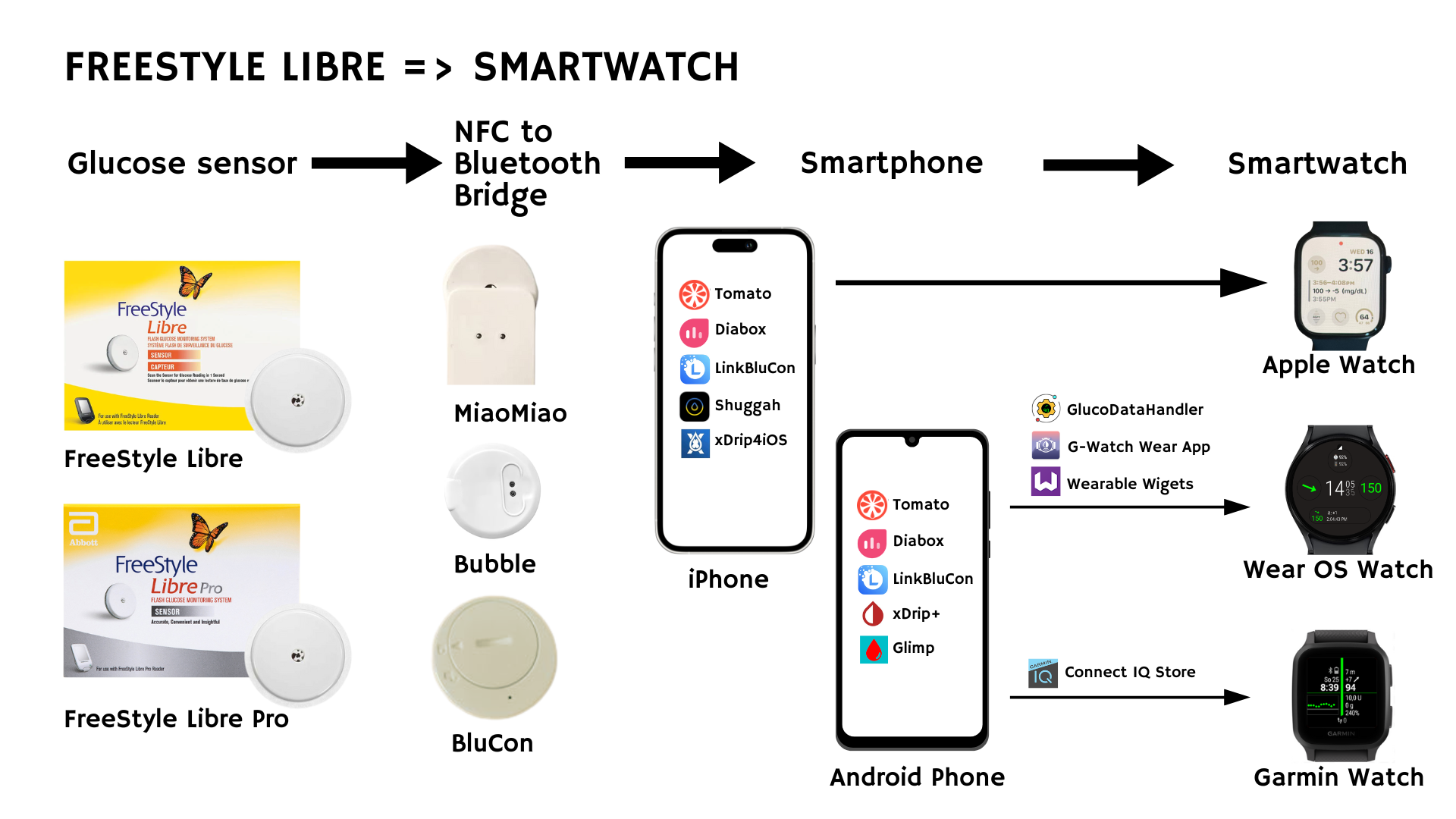
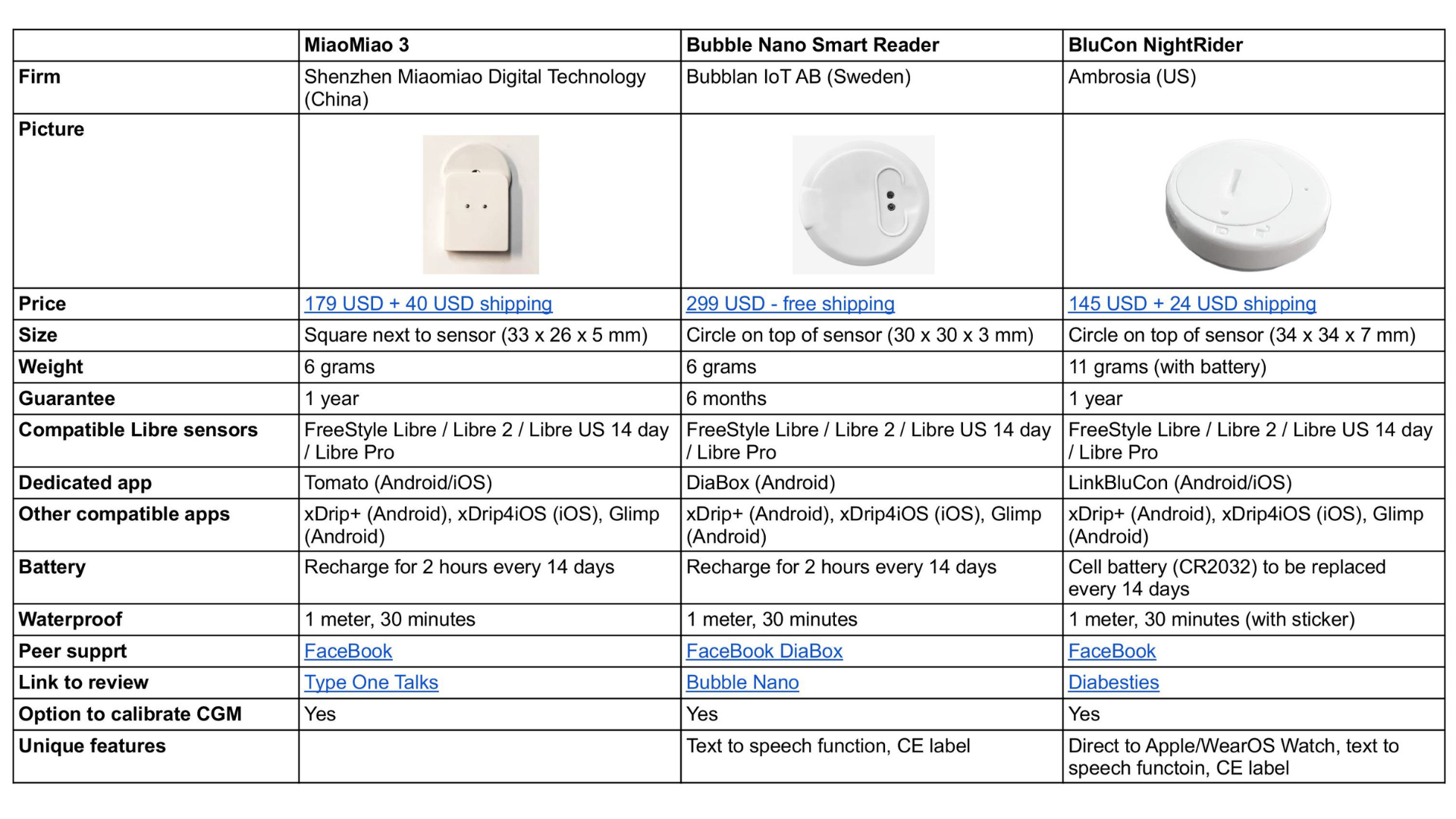
Libre (Pro) sensors transmit data only via NFC scanning, so to get continuous readings, you need an NFC-to-Bluetooth bridge (e.g., MiaoMiao, Bubble, or BluCon). Alternatively, a custom-built NFC-to-Bluetooth bridge, known as a LimiTTer, can be used, though this approach is uncommon.
Setup Steps
- Attach an NFC-to-Bluetooth transmitter (MiaoMiao, Bubble, or BluCon) to your Libre (Pro) sensor.
- Install a compatible app on your phone: Tomato (for MiaoMiao), Diabox (for Bubble), or LinkBluCon (for BluCon).
- Optional: For advanced features or watch integration, consider open-source apps like xDrip+ (Android), Glimp (Android), Shuggah (iOS), or xDrip4iOS (iOS).
Apple Watch Integration
- Install the companion Apple Watch app (Tomato, LinkBluCon, Shuggah, xDrip4iOS) and add a corresponding complication to your watch face.
Samsung (Wear OS) Integration
- If the corresponding phone app offers a Wear OS companion (e.g., LinkBluCon WearOS), install it on your watch.
- Alternatively, use bridging apps (GlucoDataHandler, G-Watch Wear App, Wearable Widgets) to pull data from xDrip+, Diabox, or Glimp.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link xDrip+ to GlucoDataHandler. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. Some additional settings in Diabox or xDrip+ might be necessary. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
- Wearable Widgets: Diabox is available as a widget via the Wearable Widgets app, a tutorial can found here.
Garmin Integration
- Use Diabox, xDrip+, or Glimp as a data hub on your Android phone.
- Install a Garmin watch face, widget or Data Field from the Connect IQ store (e.g., by andreas-may, Horsetooth, John_ and Roboleo1010) that can pull data from xDrip+ or Diabox.
5.2 FreeStyle Libre 2 (Plus)
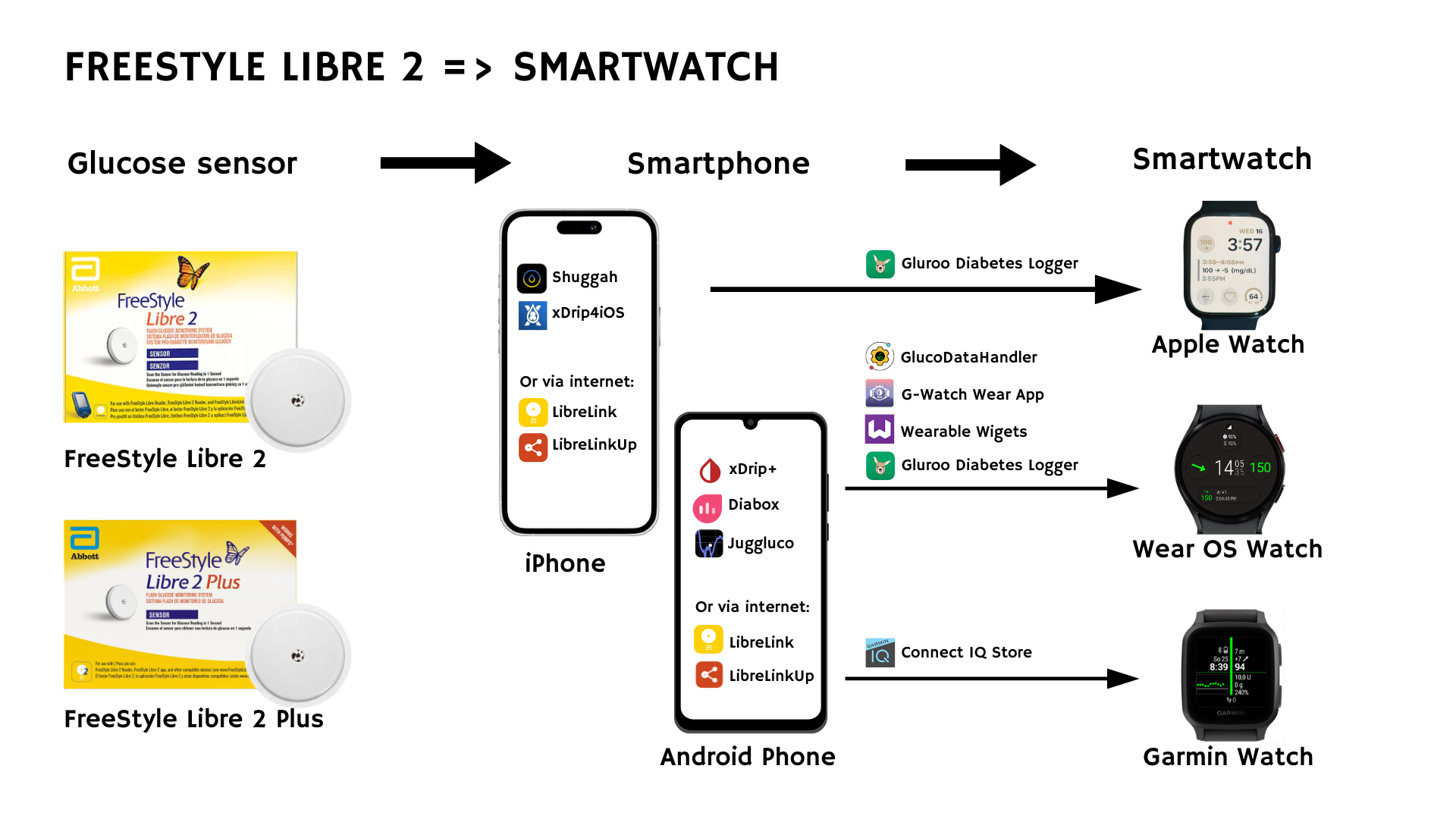
Abbott’s Libre 2 sensors vary by region. Some require scanning; others stream data automatically (e.g. FreeStyle Libre 2 Plus sensors, or via the updated LibreLink app). None currently have official watch integration, so we rely on open-source apps or community workarounds.
Offline Integration (No Internet Required)
- Deactivate the native Libre app’s Bluetooth after starting the sensor (so the open-source app can bind to the sensor).
- Install an open-source app on your phone:
- Android: Juggluco, xDrip+, Diabox (for EU sensors only).
- iOS: Shuggah, xDrip4iOS (for EU sensors only).
- Start the sensor in the open-source app, to directly read the Libre 2 data.
- Juggluco: more information can be found on their webpage and GitHub page.
- xDrip+: more information can be found on their documentation page.
- xDrip4iOS: more information can be found on their documentation page.
Apple Watch (via Shuggah)
- Install Shuggah on iPhone/Watch. Set Libre 2 Direct as the CGM source. A tutorial can be found here.
- Add Shuggah as a watch face complication.
Samsung Watch (Wear OS)
- Use Juggluco, xDrip+, or Diabox on your Android phone.
- Install Juggluco on both phone and watch, or use a bridging app (GlucoDataHandler, G-Watch Wear App or Wearable Widgets)
- Juggluco Wear OS: more information about Juggluco as a watch face or compilation can be found here.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link xDrip+ to GlucoDataHandler. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. Some additional settings in Diabox or xDrip+ might be necessary. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
- Wearable Widgets: Diabox is available as a widget via the Wearable Widgets app, a tutorial can found here.
Garmin
- As with Wear OS, set up Juggluco, Diabox, or xDrip+ on your Android phone.
- Install a Garmin watch face or widget from Connect IQ that connects to the open-source app’s data (e.g., by andreas-may, Horsetooth, John_, bruder_jacob of Roboleo1010).
Via LibreLinkUp (Requires Internet)
- Keep your sensor paired with the official Libre app, then create a second LibreLinkUp account as a “follower.” (This can be your personal account, provided you use a different email than the one tied to your LibreView.)
- Use an app like Glucodatahandler (Android), Gluroo Diabetes Logger (iOS or Android) or a dedicated Garmin watch app, logging in with your LibreLinkUp credentials.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link your Libre sensor to GlucoDataHandler via LibreLinkUp. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- Gluroo: a tutorial on how to connect your Libre sensor can be found here. A tutorial on how to connect Gluroo to your smartwatch can be found here. A video tutorial to connect your Libre sensor to an Apple Watch via LibreLinkUp can be found here.
- Some third-party Garmin Connect IQ apps, e.g. from bruder_jacob, can directly connect with your LibreLinkUp account.
- Data is fetched from the cloud, then displayed on your watch.
5.3 FreeStyle Libre 3 (Plus)

Libre 3 can stream data directly to Abbott’s native phone app without scanning. However, no official watch app exists yet.
- Android: Juggluco directly supports Libre 3.
- iPhone: No direct open-source connection yet, so the main workaround is LibreLinkUp.
Offline Integration (Android only)
- Disable the official Libre 3 app’s Bluetooth.
- Use Juggluco to start the sensor and collect the sensor data in the Juggluco app.
- More information can be found on their webpage and GitHub page.
- Juggluco allows sending the data to LibreView, so your healthcare provider can still see the reports.
Wear OS (Samsung)
- Install Juggluco on both phone and watch, or use a bridging app (GlucoDataHandler).
- Juggluco Wear OS: more information about Juggluco as a watch face or compilation can be found here.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link Juggluco to GlucoDataHandler. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
Garmin
- Install Juggluco on an Android phone, plus a Garmin companion app (Kerfstok) on your Garmin watch via the Connect IQ store.
Via LibreLinkUp (Requires Internet)
- Keep your sensor paired with the official Libre app, then create a second LibreLinkUp account as a “follower.” (This can be your personal account, provided you use a different email than the one tied to your LibreView.)
- Use Glucodatahandler (Android) or Gluroo Diabetes Logger (iOS or Android) to display cloud-based readings on your watch.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link your Libre sensor to GlucoDataHandler via LibreLinkUp. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- Gluroo: a tutorial on how to connect your Libre sensor can be found here. A tutorial on how to connect Gluroo to your smartwatch can be found here. A video tutorial to connect your Libre sensor to an Apple Watch via LibreLinkUp can be found here.
- Some third-party Garmin apps, e.g. from bruder_jacob, can directly connect with your LibreLinkUp account.
- Data is fetched from the cloud, then displayed on your watch.
Note for CamAPS or mylife Loop users
- If you use the FreeStyle Libre 3 in combination with the (mylife) CamAPS FX app, you can use your sensor within the native app, and send your glucose data to your smartwatch through xDrip+.
- To do this, install xDrip+ and set the data source to “Companion app.”
- Check the chapter about FreeStyle Libre 2 on how to get the glucose data from xDrip+ to your smartwatch.
5.4 Dexcom G6
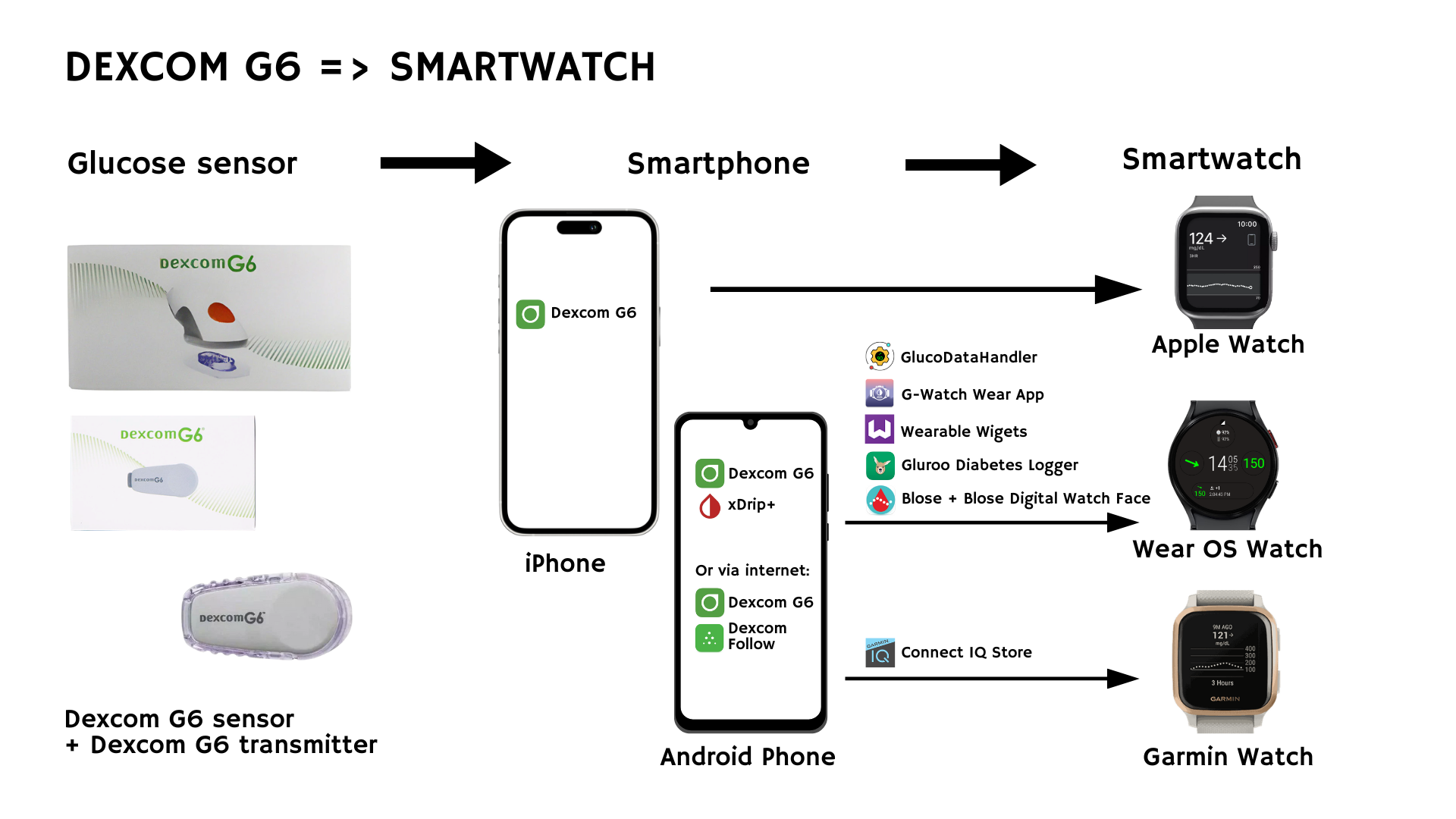
Dexcom G6 offers official apps with some watch support (e.g., Apple Watch). For Wear OS and Garmin, you can choose between direct methods (xDrip+ Companion) or Dexcom Share (internet-based).
Apple Watch
- Native: Install the Dexcom G6 app on your iPhone, which includes an Apple Watch companion app. This app also offers a dedicated Dexcom complication. More information can be found on the website of Dexcom, and a video tutorial can be here and here.
Samsung (Wear OS)
- Offline (No Internet)
- Install Dexcom G6 on your phone and use your sensor with the native app.
- Install xDrip+ and set the data source to “Companion app.”
- Use bridging apps (GlucoDataHandler or G-Watch Wear) to show glucose on your watch.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link xDrip+ to GlucoDataHandler. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. Some additional settings in xDrip+ might be necessary. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
- Internet (Dexcom Share)
- Enable Dexcom Share by inviting yourself as a follower. Then, accept the invitation in the Dexcom Follow app (you can uninstall it afterward if desired).
- On your watch, install Blose, GlucoDataHandler, G-Watch Wear, or Gluroo, and log in with your Dexcom Share credentials to stream CGM data from the cloud.
- Blose: more information can be found on their GitHub page and a video tutorial here. Due to an update with Wear OS 5, you’ll also need to download the Blose Digital Watch face on your watch, where you can host the Blose complications.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link your Dexcom sensor to GlucoDataHandler via Dexcom Share. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
- Gluroo: more information on how to connect your Dexcom sensor can be found here. A tutorial on how to connect Gluroo to your Wear OS watch can be found here.
Garmin
- Offline: Dexcom’s Connect IQ app or a custom xDrip+ watch face.
- Dexcom’s native Garmin integration:
- Dexcom offers a Dexcom app, Dexcom widget and Dexcom Data Field that can be installed on your Garmin watch via the Connect IQ app.
- A Dexcom complication can also be installed on the Face It watch face. A tutorial can be found here.
- Through xDrip+
- Install Dexcom G6 on your phone and use your sensor with the native app. Install xDrip+ and set the data source to “Companion app.”
- Install a Garmin watch face or widget from Connect IQ that connects to the xDrip’s data (e.g., by andreas-may, Horsetooth, John_, bruder_jacob or Roboleo1010).
- Dexcom’s native Garmin integration:
- Online (Dexcom Share):
- Enable Dexcom Share by inviting yourself as a follower.
- Accept the invitation in the Dexcom Follow app (you can uninstall it afterward if desired).
- Install a Garmin watch face or widget from Connect IQ that connects to the Dexcom Share’s data (e.g., by Fredrik_S, John_ or bruder_jacob). For more details and setup guides, check the description in the Connect IQ Store.
5.5 Dexcom ONE
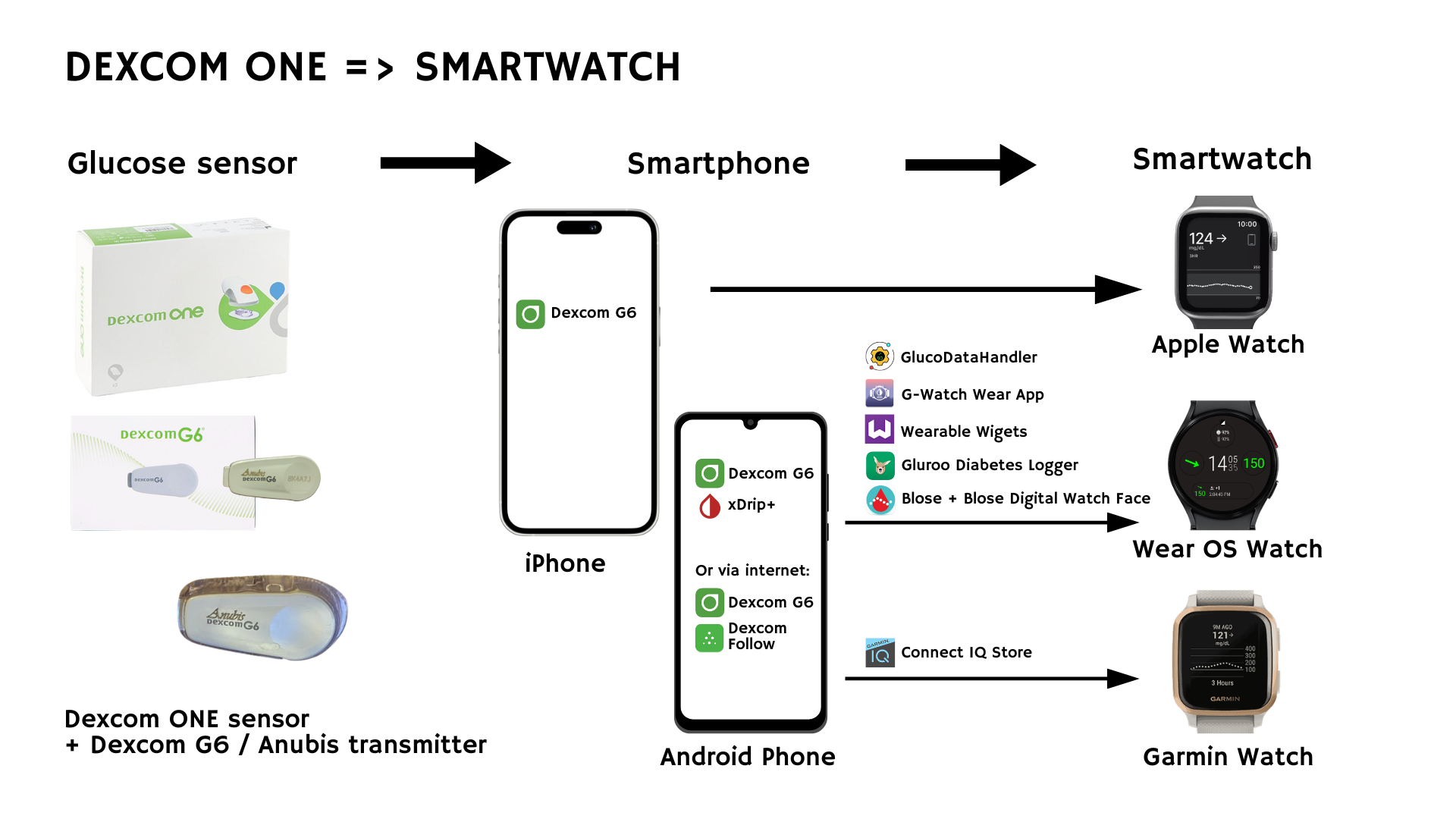
Dexcom ONE is usually locked out of Dexcom Share and watch integrations. A workaround is to use a Dexcom G6 transmitter or an Anubis transmitter paired with Dexcom ONE sensors, effectively converting them into a “G6-like” setup.
- Risks: This is off-label and not endorsed by Dexcom.
- Calibration Codes: Must be converted if mixing Dexcom ONE sensors and G6 transmitters. More information about the calibration code conversion can be found here.
If you transform a Dexcom ONE sensor into a Dexcom G6 sensor in this way, you can follow the steps in the chapter about Dexcom G6 to see the glucose values directly on your smartwatch.
5.6 Dexcom G7

Dexcom G7 offers an official Apple Watch companion app and a native Garmin integration (similar to Dexcom G6), plus an additional direct-to-Apple Watch connectivity.
Apple Watch
- Native: The Dexcom G7 iPhone app includes a watch complication and 3-hour glucose history. More information can be found on the website of Dexcom, and a video tutorial can be here and here.
Samsung (Wear OS)
- Offline (No Internet)
- Install an open-source app on your phone:
- xDrip+: Use the native Dexcom G7 app and set the data source of xDrip+ to “Companion app.”
- Juggluco: Start the Dexcom G7 sensor with Juggluco and collect the sensor data in the Juggluco app. More information can be found on their webpage and GitHub page. Be aware that Juggluco does not send data to Dexcom Clarity, which can be an issue for your healthcare provider.
- Install Juggluco on both phone and watch, or use a bridging app (GlucoDataHandler or G-Watch Wear).
- Juggluco Wear OS: more information about Juggluco as a watch face or compilation can be found here.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link xDrip+ to GlucoDataHandler. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. Some additional settings in xDrip+ might be necessary. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
- Internet (Dexcom Share)
- Enable Dexcom Share by inviting yourself as a follower. Then, accept the invitation in the Dexcom Follow app (you can uninstall it afterward if desired).
- On your watch, install Blose, GlucoDataHandler, G-Watch Wear, or Gluroo, and log in with your Dexcom Share credentials to stream CGM data from the cloud.
- Blose: more information can be found on their GitHub page and a video tutorial here. Due to an update with Wear OS 5, you’ll also need to download the Blose Digital Watch face on your watch, where you can host the Blose complications.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link your Dexcom sensor to GlucoDataHandler via Dexcom Share. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
- Gluroo: more information on how to connect your Dexcom sensor can be found here. A tutorial on how to connect Gluroo to your Wear OS watch can be found here.
Garmin
- Offline: Dexcom’s Connect IQ app or a custom Juggluco or xDrip+ watch face.
- Dexcom’s native Garmin integration:
- Dexcom offers a Dexcom app, Dexcom widget and Dexcom Data Field that can be installed on your Garmin watch via the Connect IQ app.
- A Dexcom complication can be installed on the Face It watch face. A tutorial can be found here.
- Through Juggluco:
- Download Juggluco and start the Dexcom G7 sensor with Juggluco. More information can be found on their webpage and GitHub page. Be aware that Juggluco does not send data to Dexcom Clarity, which can be an issue for your healthcare provider.
- Through xDrip+
- Install Dexcom G7 on your phone and use your sensor with the native app. Install xDrip+ and set the data source to “Companion app.”
- Install a Garmin watch face or widget from Connect IQ that connects to the xDrip’s data (e.g., by andreas-may, Horsetooth, bruder_jacob, John_ or Roboleo1010).
- Online (Dexcom Share):
- Enable Dexcom Share by inviting yourself as a follower.
- Accept the invitation in the Dexcom Follow app (you can uninstall it afterward if desired).
- Install a Garmin watch face or widget from Connect IQ that connects to the Dexcom Share’s data (e.g., by Fredrik_S, John_ or bruder_jacob). For more details and setup guides, check the description in the Connect IQ Store.
5.7 Dexcom ONE Plus

Dexcom ONE Plus offers the same smartwatch compatibility as Dexcom G7. Please refer to the methods outlined in that section.
- Apple Watch: Install Dexcom ONE Plus iPhone app + watch companion.
- Wear OS: Use direct xDrip+ or Juggluco methods, or Dexcom Share if you enable it.
- Garmin Watch: Install the Dexcom app, Dexcom widget and/or Dexcom Data Field from the Connect IQ store.
5.8 Guardian 3 / 4 (Medtronic)
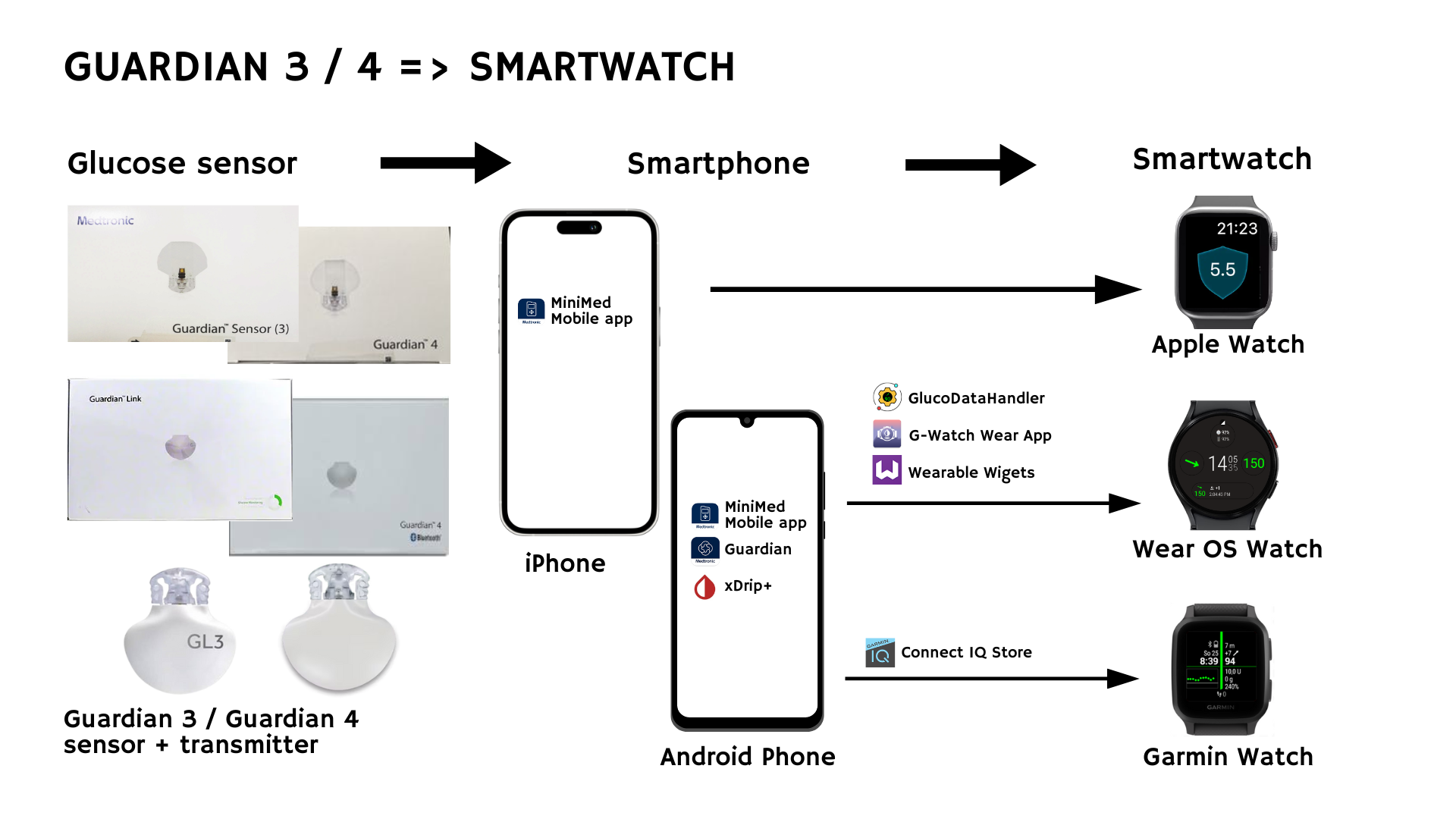
Medtronic Guardian sensors connect with Guardian or MiniMed Mobile apps. Some native watch features exist if you use the MiniMed 780G pump system.
Apple Watch
- If using MiniMed 780G, the MiniMed Mobile iOS app includes an Apple Watch companion, displaying glucose, SmartGuard status, and Time in Range. A tutorial can be found here.
Samsung (Wear OS) & Garmin
- Offline (No Internet)
- Install the MiniMed Mobile or Guardian app on your phone and use your sensor with the native app.
- Install xDrip+ and set the data source to “Companion app.”
- Use bridging apps (GlucoDataHandler or G-Watch Wear) to show glucose on your watch.
- GlucoDataHandler: link to their GitHub page and video tutorial on how to link xDrip+ to GlucoDataHandler. GlucoDataHandler offers a complication with continuous glucose data, but you can also choose a dedicated watch face made by Diabetic Masked Man.
- G-Watch Wear App: link to GitHub page and a video tutorial. Some additional settings in xDrip+ might be necessary. The G-Watch Wear app offers 2 watch faces, but you can also set up the G-Watch Wear app data as a complication using the Wearable Widgets app. Tutorials on this integration can be found here and here.
Garmin
- Offline:
- Install the MiniMed Mobile or Guardian app on your phone and use your sensor with the native app.
- Install xDrip+ and set the data source to “Companion app.”
- Install a Garmin watch face or widget from Connect IQ that connects to the xDrip’s data (e.g., by andreas-may, Horsetooth, bruder_jacob, John_ of Roboleo1010).
5.9 Simplera CGM / Sync
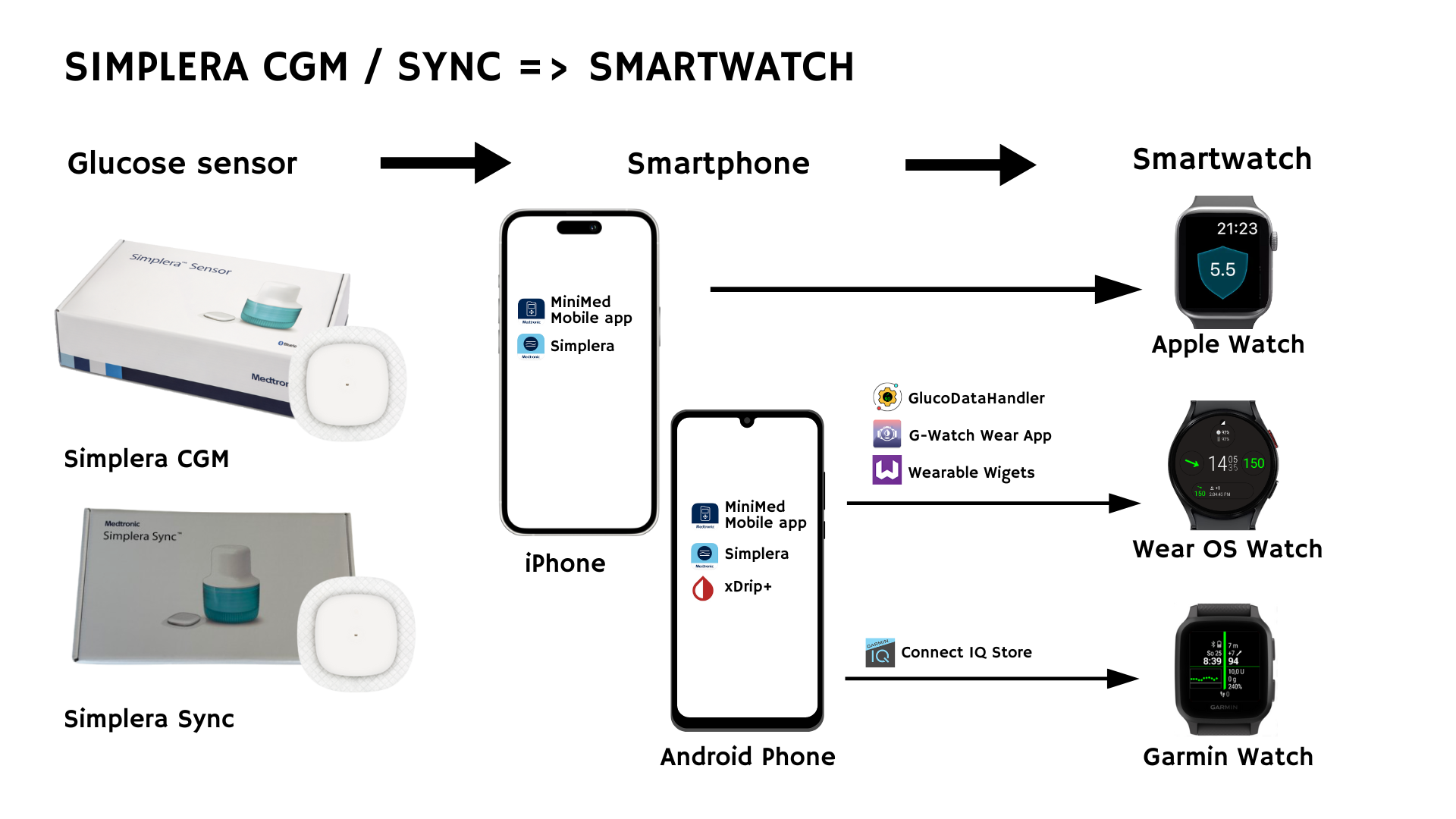
Simplera offers the same smartwatch compatibility as Guardian 3 / 4. Please refer to the methods outlined in that section.
- Apple Watch: Install the MiniMed Mobile iOS app or Simplera iOS app + watch companion.
- Wear OS & Garmin: Install xDrip+, set “Companion app” as data source, then use bridging apps (GlucoDataHandler, G-Watch, or Garmin watch faces).
5.10 Other CGMs
For lesser-known or regional CGMs (Sibionics, LinX/Aidex, CareSens, Eversense, Ottai etc), xDrip+ or Juggluco are the main bridging apps. Once recognized by xDrip+ or Juggluco, you can typically forward glucose data to your watch via the same bridging methods discussed above.
Here are the options for other CGMs in more detail:
- Sibionics: Juggluco can connect to the native Sibionics app from Chinese market Sinionics GS1Sb sensors, and also offers a direct-to-SiWatch option. xDrip+ can link to a patched version of the Sibionics app, and the xDrip Companion mode seems to be able to connect to the native Sibionics app. Another option is to create a Sibioincs follower account and use this to bring your glucose data to your smartwatch e.g. via the CGM Connect Watchface for Garmin watches.
- LinX / Aidex: xDrip+ in Companion mode can receive data from the native GlucoRX / Aidex / LinX app
- CareSens Air: toggle on data transmission to xDrip+ in the native CareSens Air app to receive glucose data in xDrip+ via the 640G/Eversense data source.
- Eversense: xDrip+ in Companion mode or 640G / Eversense can receive data from the patched Eversense app. More information can be found here.
- Ottai CGM: xDrip+ in Companion mode should be able to receive data from the native Ottai CGM app
- Stelo: xDrip in Companion mode can receive data from the native Stelo app. Note: the native Stelo app only gives readings every 15 minutes.
- Accu-Check SmartGuide CGM: Roche offers a native Apple Watch integration.
6. The Present and Future of Direct CGM-to-Smartwatch Connectivity
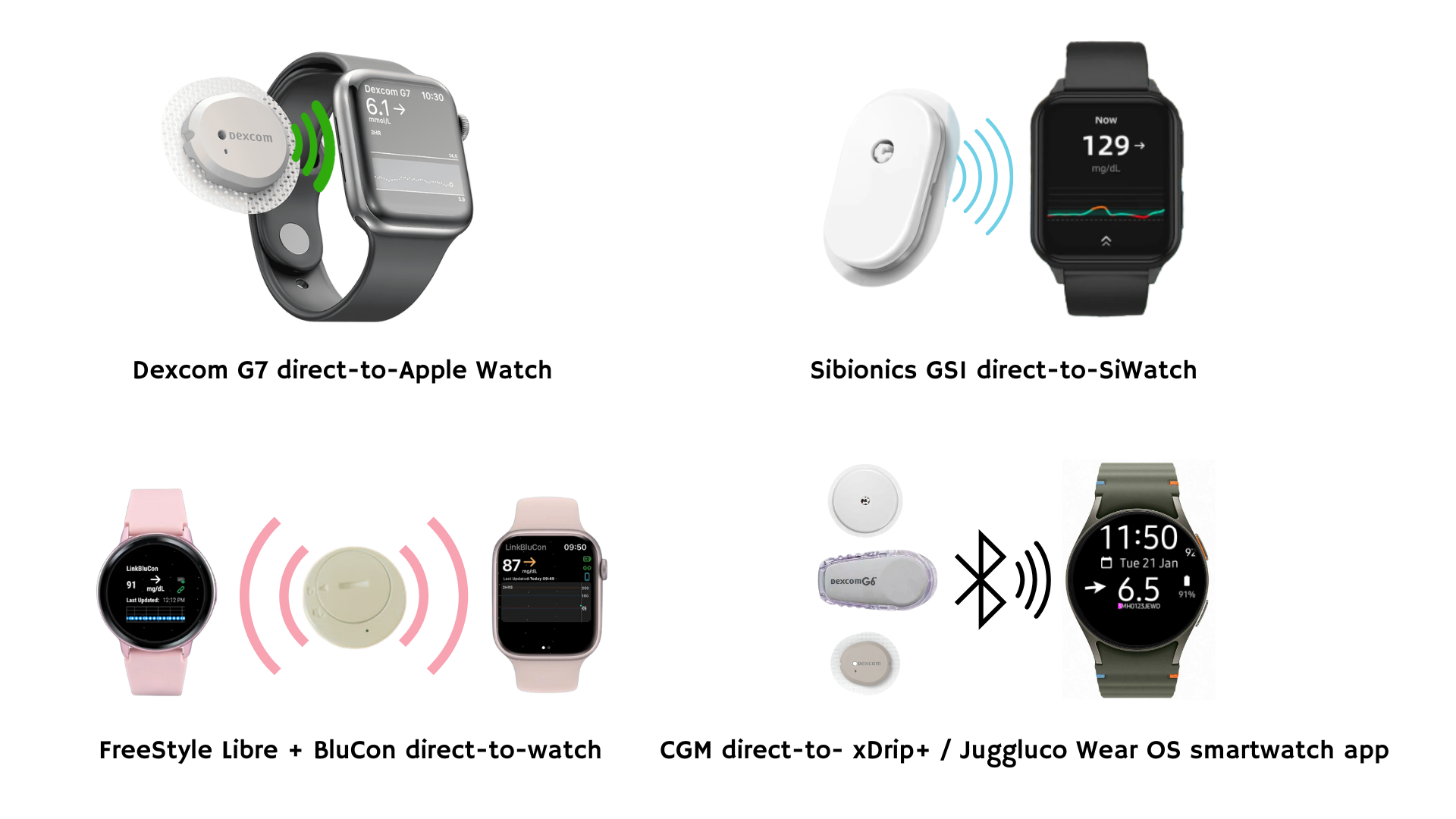

The ability to check CGM data directly on a smartwatch—without needing a phone—remains a highly sought-after feature for people living with diabetes. While full phone-free CGM integration is still developing, several partial solutions are available as of early 2025:
- Dexcom G7 + Apple Watch → The only official direct-to-watch solution, allowing Bluetooth connection between the sensor and an Apple Watch (Series 6 or later, watchOS 10+).
- Sibionics GS1 + SiWatch → A dedicated smartwatch for GS1 CGMs, offering real-time glucose tracking via Bluetooth.
- Libre 1/Pro/2 + BluCon NightRider → A transmitter add-on that enables continuous readings on Apple, Android, and Fitbit smartwatches using the LinkBluCon app.
- Open-Source (xDrip+, Juggluco) → Community-driven apps allow multiple sensors to send data to Android Wear OS watches, though setup requires technical expertise and carries no regulatory approvals.
Challenges of Current Direct-to-Watch Solutions
- Initial Phone Setup → Even with direct smartwatch connections, all CGMs still require a phone for initial sensor activation and configuration.
- Battery Drain → Continuous Bluetooth streaming significantly reduces smartwatch battery life.
- Limited Compatibility → Direct-to-watch solutions are mostly exclusive to certain devices (e.g., Dexcom G7 for Apple Watch, Sibionics for SiWatch).
The Future of CGM-to-Watch Connectivity
Industry experts anticipate three major developments by 2026:
- Next-Generation Sensors → Future CGMs may feature built-in LTE modems or advanced BLE protocols to support true phone-free smartwatch integration.
- Standardized APIs → The development of universal data-sharing standards will improve the compatibility of smartwatches from different brands.
- AI-Driven Insights → Future watches may analyze glucose trends alongside heart rate variability, activity and sleep data, providing better glucose predictions for better glucose control.
Although full smartphone independence isn't possible yet, today's workarounds already allow you to stream your CGM data directly to your smartwatch.
7. The Dream of Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring

For decades, researchers and tech giants like Apple, Samsung, and Huawei have pursued the holy grail of glucose monitoring—a non-invasive sensor that measures blood sugar without piercing the skin. Several promising technologies have been explored, including:
- Raman Spectroscopy – Using laser-based skin analysis to detect glucose-specific molecular signals.
- Radiofrequency & Microwave Sensors – Using electromagnetic waves to detect glucose by analyzing changes in tissue’s electrical properties.
- Optical & PPG Sensors – AI-enhanced multi-wavelength LEDs estimating glucose from changes in light absorption and blood flow patterns.
Despite breakthroughs in early testing, as of March 2025, no mass-market smartwatch offers a clinically approved, non-invasive CGM. The challenge lies in physiological variability, regulatory approval, and sensor accuracy—issues that have derailed past attempts.
However, AI-driven innovations are accelerating progress. Machine learning is improving signal processing to separate glucose data from other biological noise, and predictive modeling may soon integrate glucose trends with heart rate and sleep data.
While commercial non-invasive CGMs remain just out of reach, industry experts anticipate a breakthrough within the next 2–5 years. The dream of truly painless, wearable glucose tracking is no longer a question of if, but when—and which company will get there first.
8. Practical Considerations & Troubleshooting
#1 Community Resources
Getting CGM data on your smartwatch can be tricky, but you're not alone. Join online communities like Facebook groups, Discord servers, or Telegram channels (e.g., Looped, xDrip+, or brand-specific groups) for real-time support and troubleshooting tips.
#2 Battery Management
-
Continuous Bluetooth scanning can shorten watch and phone battery life.
-
Reduce battery usage by adjusting alert thresholds or extending update intervals if needed.
#3 Partial Solution: Notifications Only
-
If full data display is too complex, mirror CGM alerts on your watch instead.
-
For exercise, consider setting low-glucose alerts slightly higher (e.g., 90 mg/dL or 5.0 mmol/L) to catch drops earlier.
9. Conclusion and Additional Resources

By combining official apps, open-source solutions, and dedicated hardware bridges, it’s now feasible to view CGM data on virtually any modern smartwatch. While Dexcom and Medtronic users enjoy some native features, those using FreeStyle Libre or lesser-known CGMs can still achieve similar integrations through creative workarounds.
- Always remain vigilant about safety and accuracy; open-source tools carry inherent risks and are not medically approved. If in doubt, get your meter out!
- For more details or step-by-step examples, consider joining relevant online communities or consult your diabetes care team.
- If you’d like to share these instructions directly with patients, you can share a downloadable PDF of this article [HERE].
Empower yourself and your patients to check glucose data discreetly and conveniently on a smartwatch—improving quality of life and facilitating more proactive diabetes management.
Kind regards,